
Health Library
What is Silver Sulfadiazine: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects and More
October 10, 2025
Question on this topic? Get an instant answer from August.
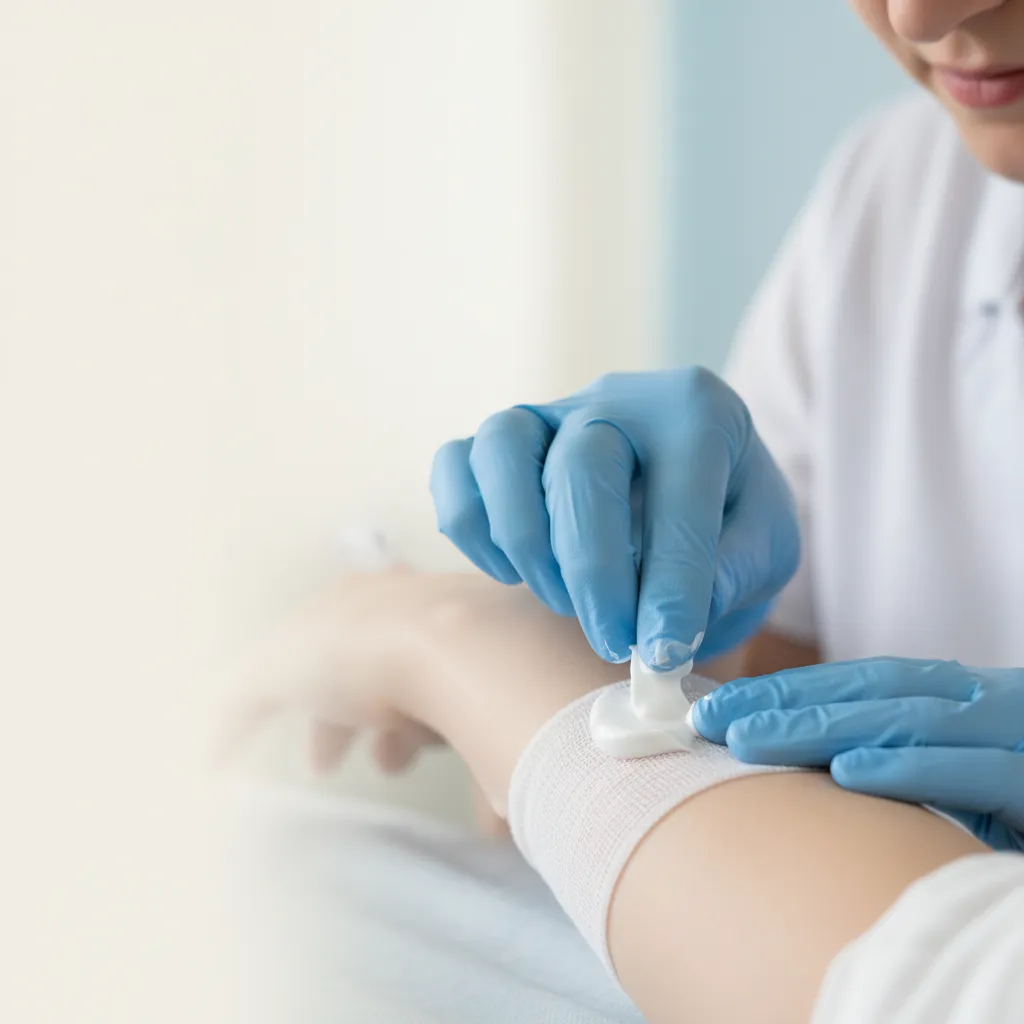
Silver sulfadiazine is a topical antibiotic cream that helps prevent and treat infections in burns and wounds. This medication combines silver with sulfadiazine, creating a powerful barrier against harmful bacteria that could otherwise slow healing or cause serious complications.
Healthcare providers commonly prescribe this cream because it's particularly effective at protecting vulnerable skin while it heals. You'll often encounter it in burn treatment centers and wound care clinics, where preventing infection is absolutely crucial for proper recovery.
What is Silver Sulfadiazine Used For?
Silver sulfadiazine primarily treats second and third-degree burns, helping prevent bacterial infections that could turn a manageable injury into a life-threatening situation. The medication works as both a treatment for existing infections and a preventive shield against new bacterial growth.
Beyond burns, doctors sometimes prescribe this cream for other serious wounds that are at high risk of infection. These include pressure ulcers, diabetic foot wounds, and surgical sites that aren't healing properly. The cream creates a protective barrier that keeps harmful bacteria from taking hold while your body's natural healing processes do their work.
In some cases, healthcare providers use silver sulfadiazine for infected skin grafts or areas where the skin has been severely damaged by trauma. The medication helps create an environment where healthy tissue can grow back without interference from bacterial invaders.
How Does Silver Sulfadiazine Work?
Silver sulfadiazine works by slowly releasing silver ions that penetrate bacterial cell walls and disrupt their ability to reproduce and survive. This dual-action approach makes it particularly effective against a wide range of bacteria, including some that resist other antibiotics.
The medication is considered a moderately strong topical antibiotic, more powerful than basic over-the-counter options but gentler than some systemic antibiotics. It doesn't just kill bacteria on the surface but actually penetrates into the wound tissue, providing deeper protection where it's needed most.
What makes this medication special is its sustained-release formula. Rather than delivering all its antibacterial power at once, it continues working for hours after application, giving your skin consistent protection throughout the day and night.
How Should I Take Silver Sulfadiazine?
Apply silver sulfadiazine cream directly to the affected area using clean hands or sterile gloves, spreading it evenly in a thin layer about 1/16 inch thick. Your healthcare provider will show you the proper technique during your first visit, ensuring you understand how much to use and how to apply it safely.
Before each application, gently clean the wound area with saline solution or as directed by your doctor. This removes any debris, old medication, or dead tissue that might interfere with the cream's effectiveness. Pat the area dry with a clean cloth before applying the new layer.
You don't need to take this medication with food or water since it's applied topically rather than swallowed. However, timing your applications around your daily routine can help ensure consistent treatment. Many people find it helpful to apply the cream after their morning shower and again before bedtime.
Always wash your hands thoroughly both before and after applying the cream. If you're treating a burn or wound on your hands, have someone else help you apply the medication to ensure proper coverage without contaminating the area.
How Long Should I Take Silver Sulfadiazine For?
Most people use silver sulfadiazine for anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the severity of their burn or wound and how quickly it heals. Your doctor will monitor your progress and adjust the treatment duration based on how well your skin is responding.
For minor burns, you might only need the cream for 7-10 days until new skin forms and the infection risk decreases. More severe burns or complex wounds may require several weeks of treatment, especially if you're dealing with deeper tissue damage that takes longer to heal.
Your healthcare provider will schedule regular follow-up appointments to assess your healing progress. They'll look for signs that the wound is closing properly, check for any signs of infection, and determine when it's safe to stop using the medication.
Never stop using silver sulfadiazine abruptly without consulting your doctor, even if the wound looks better. Stopping too early could allow bacteria to return and cause a setback in your healing process.
What Are the Side Effects of Silver Sulfadiazine?
Most people tolerate silver sulfadiazine well, but like any medication, it can cause side effects ranging from mild skin reactions to more serious complications. Understanding what to watch for helps you use the medication safely and know when to contact your healthcare provider.
Common side effects you might experience include temporary burning or stinging when you first apply the cream, along with mild skin irritation around the treated area. These reactions usually fade within a few minutes as your skin adjusts to the medication.
Here are the most frequently reported side effects that typically resolve on their own:
- Temporary burning or stinging sensation upon application
- Mild redness or irritation around the wound edges
- Slight skin discoloration that fades after treatment ends
- Increased sensitivity in the treated area
- Temporary changes in skin texture or appearance
These common reactions are usually your skin's normal response to the medication and shouldn't cause concern unless they worsen over time.
More serious side effects require immediate medical attention, though they occur less frequently. Watch for signs of allergic reactions, including severe itching, widespread rash, or difficulty breathing. Some people develop blue-gray skin discoloration called argyria, which can be permanent if the medication is used for extended periods.
Contact your doctor right away if you experience any of these concerning symptoms:
- Severe allergic reactions like hives, swelling, or trouble breathing
- Signs of kidney problems, including changes in urination patterns
- Blood disorders symptoms like unusual bruising or fatigue
- Persistent blue-gray skin discoloration
- Worsening infection signs like increased redness, warmth, or pus
- Fever or chills that develop during treatment
These serious side effects are rare but can be dangerous if left untreated, so don't hesitate to seek medical help if you're concerned.
Some people may experience rare but significant complications like decreased white blood cell counts or liver function changes. Your doctor may order periodic blood tests if you're using the medication for extended periods to monitor for these potential issues.
Who Should Not Take Silver Sulfadiazine?
Silver sulfadiazine isn't safe for everyone, and certain health conditions or circumstances make this medication inappropriate or potentially dangerous. Your doctor will carefully review your medical history before prescribing this cream to ensure it's the right choice for your situation.
People with known allergies to silver, sulfadiazine, or other sulfa drugs should avoid this medication entirely. Even a small amount could trigger a serious allergic reaction that might require emergency medical treatment.
Pregnant women, especially those in their third trimester, typically shouldn't use silver sulfadiazine because it can potentially harm the developing baby. The medication can cross into breast milk, so nursing mothers usually need alternative treatments to avoid exposing their infants to unnecessary risks.
Several medical conditions make silver sulfadiazine unsuitable or require special precautions before use:
- Severe kidney disease or kidney failure
- Liver disease or impaired liver function
- Blood disorders like anemia or low white blood cell counts
- G6PD deficiency, a genetic enzyme disorder
- Severe burns covering large areas of the body
- Premature infants or newborns under 2 months old
These conditions can increase your risk of serious side effects or make it harder for your body to process the medication safely.
Certain medications can interact with silver sulfadiazine, potentially causing dangerous complications. Tell your doctor about all medications you're taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter products, and herbal supplements. This information helps them determine if silver sulfadiazine is safe for you or if you need an alternative treatment.
Silver Sulfadiazine Brand Names
Silver sulfadiazine is available under several brand names, with Silvadene being the most widely recognized and commonly prescribed version. This brand has been trusted by healthcare providers for decades and maintains consistent quality standards that doctors rely on.
Other brand names include Thermazene and SSD Cream, which contain the same active ingredient but may have slightly different inactive ingredients or packaging. Your pharmacy might carry different brands depending on their supplier relationships and your insurance coverage.
Generic versions of silver sulfadiazine are also available and work just as effectively as brand-name options. These generic creams contain the same concentration of active ingredient and must meet the same safety and efficacy standards set by regulatory authorities.
Silver Sulfadiazine Alternatives
Several alternative treatments can effectively manage burns and wounds when silver sulfadiazine isn't suitable or available. Your healthcare provider will consider your specific situation, medical history, and the type of wound you're treating when recommending alternatives.
Bacitracin and mupirocin are popular topical antibiotics that work well for smaller wounds and burns. These medications offer good bacterial coverage with potentially fewer side effects, though they may not be as effective for severe burns or large wound areas.
Modern wound care often incorporates advanced dressings that contain silver or other antimicrobial agents. These products include silver-impregnated foam dressings, hydrogel sheets, and antimicrobial barrier films that provide continuous protection while promoting healing.
For patients who can't use sulfa-based medications, healthcare providers might recommend:
- Polysporin or other antibiotic ointments without sulfa
- Honey-based wound dressings with natural antimicrobial properties
- Iodine-based solutions for wound irrigation and protection
- Advanced wound care products like collagen dressings
- Oral antibiotics for systemic infection prevention
Each alternative has its own benefits and limitations, so your doctor will help you choose the most appropriate option based on your individual needs and circumstances.
Is Silver Sulfadiazine Better Than Bacitracin?
Silver sulfadiazine and bacitracin each have distinct advantages depending on the type and severity of wound you're treating. Silver sulfadiazine is generally more effective for serious burns and larger wounds because it provides broader bacterial coverage and penetrates deeper into tissue.
For severe burns, silver sulfadiazine typically offers superior protection against the wide range of bacteria that commonly infect burn wounds. Its sustained-release formula provides longer-lasting antimicrobial activity, which is crucial when dealing with injuries that take weeks to heal.
Bacitracin works well for minor cuts, scrapes, and small burns where the infection risk is lower. It's often gentler on the skin and less likely to cause allergic reactions, making it a good choice for people with sensitive skin or those who've had problems with sulfa medications.
Your doctor will consider several factors when choosing between these medications, including the size and depth of your wound, your medical history, and any allergies you might have. Neither medication is universally better – the right choice depends on your specific situation and healing needs.
Frequently asked questions about Silver sulfadiazine (topical route)
Is Silver Sulfadiazine Safe for Diabetics?
Is Silver Sulfadiazine Safe for Diabetics?
Silver sulfadiazine can be safe for diabetics when used under proper medical supervision, though people with diabetes need extra monitoring during treatment. Diabetic wounds often heal more slowly and are at higher risk for infection, making the antimicrobial protection this medication provides particularly valuable.
However, diabetics may have an increased risk of kidney problems, which can be worsened by sulfa medications like silver sulfadiazine. Your doctor will likely monitor your kidney function more closely and may adjust your treatment plan if any concerns arise.
If you have diabetes, make sure your healthcare provider knows about your condition and any diabetes-related complications you've experienced. They may recommend alternative treatments or additional precautions to ensure your safety while treating your wound.
What Should I Do If I Accidentally Use Too Much Silver Sulfadiazine?
What Should I Do If I Accidentally Use Too Much Silver Sulfadiazine?
If you accidentally apply too much silver sulfadiazine, gently remove the excess with a clean, damp cloth and apply a fresh, thin layer as directed. Using too much cream doesn't improve healing and can actually slow the process by creating a barrier that prevents proper air circulation.
Watch for signs of increased skin irritation, such as excessive redness, burning, or swelling around the treated area. These symptoms might indicate that the heavy application is irritating your skin more than usual.
If you're concerned about the amount you applied or if you notice any unusual reactions, contact your healthcare provider for guidance. They can assess whether you need to adjust your application technique or if any additional care is needed.
What Should I Do If I Miss a Dose of Silver Sulfadiazine?
What Should I Do If I Miss a Dose of Silver Sulfadiazine?
If you miss a scheduled application of silver sulfadiazine, apply it as soon as you remember, then return to your regular schedule. Don't apply extra cream to make up for the missed dose – this won't improve your healing and might cause unnecessary irritation.
Missing occasional doses usually won't significantly impact your healing, but try to maintain consistent applications as prescribed. Set phone reminders or incorporate the applications into your daily routine to help you remember.
If you frequently forget doses, talk to your healthcare provider about strategies to improve consistency. They might adjust your dosing schedule or recommend other approaches to help you stay on track with your treatment.
When Can I Stop Taking Silver Sulfadiazine?
When Can I Stop Taking Silver Sulfadiazine?
You can stop using silver sulfadiazine when your healthcare provider determines that your wound has healed sufficiently and the infection risk has decreased. This decision should always be made by your doctor rather than based on your own assessment of the wound's appearance.
Most people can discontinue the medication when new skin has formed over the wound and there are no signs of infection. Your doctor will look for specific healing markers, such as proper tissue formation and the absence of drainage or inflammation.
Never stop using silver sulfadiazine abruptly without medical approval, even if you feel the wound looks better. Premature discontinuation can lead to bacterial regrowth and potentially serious complications that could set back your healing process significantly.
Can I Use Silver Sulfadiazine on My Face?
Can I Use Silver Sulfadiazine on My Face?
Silver sulfadiazine can be used on facial burns and wounds when prescribed by a healthcare provider, though facial application requires extra care due to the sensitive nature of facial skin. The area around your eyes, nose, and mouth needs particular attention to avoid accidental contact with these sensitive areas.
Facial wounds often heal differently than those on other parts of your body, and your doctor may recommend modified application techniques or additional precautions. They might also suggest alternative treatments that are specifically formulated for facial use.
Always follow your healthcare provider's specific instructions for facial application, and contact them immediately if you experience any unusual reactions or if the medication accidentally gets into your eyes, nose, or mouth.
Health Companion
trusted by
6Mpeople
Get clear medical guidance
on symptoms, medications, and lab reports.

